Max Rady College of Medicine
Concept: Capture-Recapture Method of Estimating Population Size
Concept Description
Last Updated: 2015-12-14
Introduction
-
This concept describes the capture-recapture method of estimating population size, as it was used to estimate the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in
Chartier et al. (2015).
This includes a general description of the capture-recapture methodology and how this methodology was applied using administrative and laboratory data available from the MCHP Data Repository. Links to the technical details and key findings from this research are also provided.
The capture-recapture method is used for "... estimating the size of a target population or a subset of this population that uses overlapping and presumably incomplete but intersecting sets of data about that population. Though the capture-recapture methods have some limitations, they are useful to estimate numbers of cases and numbers at risk in elusive populations". (Last, 2001).
Methodology
-
In Chartier et al. (2015) they used the capture-recapture method as one of three methods to estimate the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in both adults and children, based on cases defined in administrative and laboratory data. Please read the
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
concept for information on how CKD was defined using administrative and laboratory data.
The Chapman Estimator (Chapman, 1951)
In Chartier et al. (2015) they used the Chapman estimator to estimate CKD prevalence. This approach is often used in estimating the size of animal populations. This capture-recapture method was applied to the CKD data using the following general formula:
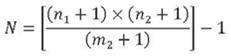
where:
N = estimate of the population sizeFor more information on this method, please read the section titled Chronic Kidney Disease Prevalence in the report.
n 1 = size of sample 1
n 2 = size of sample 2
m 2 = number in sample 2 that are also in sample 1MCHP Adaptation of the Chapman Estimator
Using the administrative data definition and lab-based definition, Chartier et al. (2015) estimated the total CKD population using the following formula:
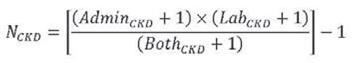
where:
N CKD = estimate of total CKD populationFor more information on how the capture-recapture method was applied in this research, please read the capture-recapture technical definition and formula from the Appendix in the report.
Admin CKD = number meeting the administrative definition April 1 2009 - March 31 2012
Lab CKD = number meeting the lab-based definition April 1 2006 - March 31 2012
Both CKD = number meeting both definitions
NOTE: The administrative data used to identify CKD included the Hospital Abstracts, Medical Services (Physician Claims) and Drug Program Information Network (DPIN) data. For more information on how CKD was defined, please read the Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) concept.
Findings and Results
-
The following results are available from the report:
-
Figure 3.2: Prevalence of Adults with Chronic Kidney Disease by Region and Estimation Method
- Table 3.2: Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease in Children by Estimation Method
For more general information, please read Chapter 3: Cohort Description: Chronic Kidney Disease and End Stage Kidney Disease which includes the key findings regarding the adult and child cohorts from this report, and specific details about these two groups.
Related concepts
Related terms
References
- Chapman DG. Some Properties of the Hypergeometric Distribution with Applications to Zoological Sample Censuses. University of California Publications in Statistics. Berkeley and Los Angeles, CA: University of California Press. 1951;1(7)131-160. 1951.(View)
- Chartier M, Dart A, Tangri N, Komenda P, Walld R, Bogdanovic B, Burchill C, Koseva I, McGowan K-L, Rajotte L. Care of Manitobans Living with Chronic Kidney Disease. Winnipeg, MB: Manitoba Centre for Health Policy, 2015. [Report] [Summary] [Updates and Errata] [Additional Materials] (View)
- Last JM. A Dictionary of Epidemiology. 4th Edition. In: Spasoff, RA, et. al. (eds). New York, New York: Oxford University Press; 2001. 0-0.(View)
Request information in an accessible format
If you require access to our resources in a different format, please contact us:
- by phone at 204-789-3819
- by email at info@cpe.umanitoba.ca
We strive to provide accommodations upon request in a reasonable timeframe.
Contact us
Manitoba Centre for Health Policy
Rady Faculty of Health Sciences,
Room 408-727 McDermot Ave.
University of Manitoba
Winnipeg, MB R3E 3P5 Canada
