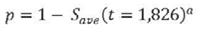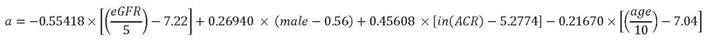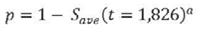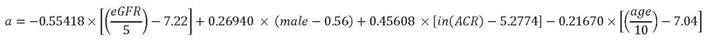Term: Kidney Failure Risk Equation (KFRE)
Glossary Definition
Last Updated: 2015-12-03
Definition:
Kidney Failure Risk Equation (KFRE) are a group of predictive models developed by
Tangri et al., 2011
that evaluate the short-term risk of progression to kidney failure among patients with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease (CKD).
The KFRE model used in Chartier et al. (2015) is based on laboratory data and demographic variables that predicts the risk of developing kidney (renal) failure. Variables include age, sex, protein levels in the urine and kidney function measured using
estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
The formulas are:
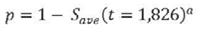
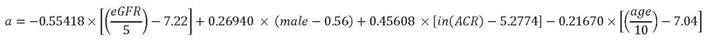
Where:
-
p = Five-year risk of kidney failure
-
S
ave
(t=1826) = Five-year survival rate for an individual with the average value of covariates in the risk equation and was 0.929 in the development dataset
-
eGFR =
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR)
(ml/min/1.73m2)
-
ln(ACR) = Natural logarithm of
Albumin-Creatinine Ratio (ACR)
(mg/g)
-
male = Indicator for sex (male = 1, female = 0)
-
age = Age (years) at test date
Related concepts
Related terms
References
-
Tangri N, Stevens LA, Griffith J, Tighiouart H, Djurdjey O, Naimark D, Levin A, Levey AS.
A predictive model for progression of chronic kidney disease to kidney failure.
JAMA
2011;305(15):1553-1559. [Abstract] (View)
Term used in
-
Chartier M, Dart A, Tangri N, Komenda P, Walld R, Bogdanovic B, Burchill C, Koseva I, McGowan K-L, Rajotte L.
Care of Manitobans Living with Chronic Kidney Disease.
Winnipeg, MB:
Manitoba Centre for Health Policy,
2015. [Report] [Summary] [Updates and Errata] [Additional Materials] (View)