ArcCatalog: BASIC USES
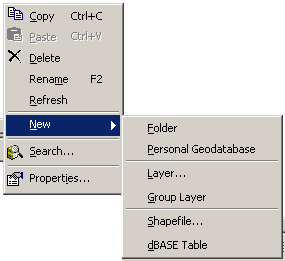
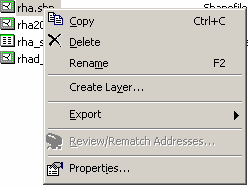
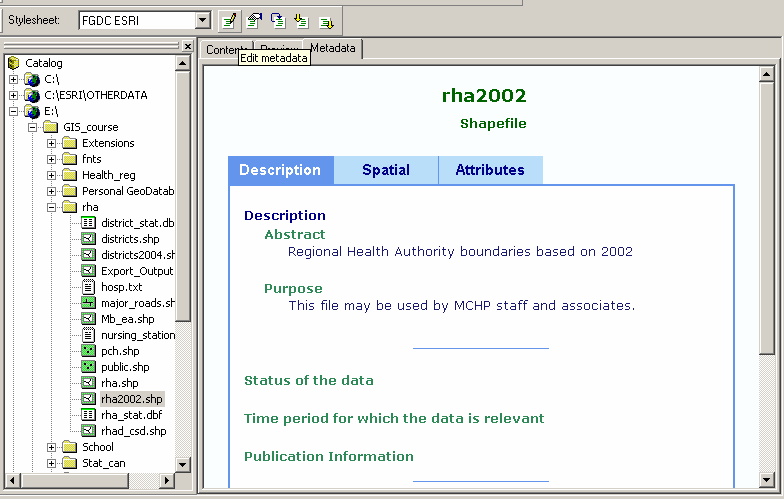
| Using ArcCatalog ArcCatalog is used for managing geographic data. You can copy, move and delete data. There are options to preview existing files and attributes. Built into ArcCatalog is the ability to create and update basic metadata for geographic files. This is also the place where you create new data files. The ArcCatalog application includes a catalog tree display, similar to windows explorer, preview window and several tool bars. In the catalog tree each data type (geodatabase, coverages, shape files, CAD files, rasters, and TINs) has its own unique icon. Preview and Metadata The catalog tree shows the available data sources both locally, and remotely. When looking at folders on the local system you must attach or connect to the folder to make it available as a local data source – in the way the ‘Add Data’ option in ArcGIS is different than the usual Windows open dialog box. The Contents window will allow users to select file properties, export, create new files, new directories, and geodatabases. If both ArcMap and ArcCatalog are open, data sources can be dropped from ArcCatalog into ArcMap. There is also a preview option that will allow you to see the geography and attribute tables. Metadata for each file can be easily created and updated for every geographic data source from within ArcCatalog. A standardized template for editing and updating metadata is provided and when files are moved within ArcCatalog the Metadata is transferred with the data. Meta data is saved as XML files in the same directory as the data source or within the associated GeoDatabase. Meta data files can also be exported for use elsewhere.
GeoDatabases A geodatabase is a relational database that contains spatial and non-spatial objects. The geodatabase supports the storage and management of geographic information in standard database management system tables (ESRI Press). A complete coverage of GeoDatabases is beyond this workshop but there has been another workshop developed at MCHP for working with GeoDatabases. There are two broad types of GeoDatabase available to ArcGIS. At MCHP, only the personal GeoDatabases are available at this time.
Internet Servers ArcGIS can query and use geographic data available on the internet. Many of these services cost money but there are a few that are free and have some very useful base information. In Canada the most common is www.geographynetwork.ca. Once attached to an internet service you can add the geography
information off of the net (from image services or feature services)
or make local copies of some files (only from feature services).
| ||||