1. When copying the map it will be copied as an ESRI Map object
with all of the detail and scalability seen in ArcGIS. The image
can be pasted directly or, optionally, pasted as an enhanced meta
file in the final document.
2. Export Map from the Edit Menu.
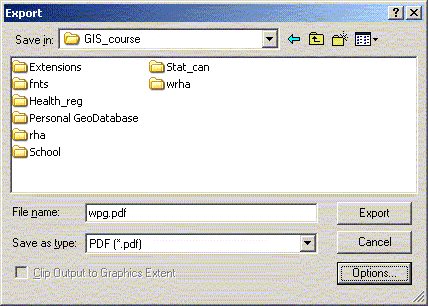
a. If you are just sending maps to other people it is usually
best to send the maps as PDF files. One of the nice benefits
of PDF files beyond being transportable they are also searchable
for text strings and generally not editable by the end user
– what you created is what they will get. ArcGIS will
directly export maps to PDF files without having to go through
a secondary PDF writer.
b. If you want to use a map in a PowerPoint presentation or
other Windows package likely you will want to export the file
as an enhanced meta file (EMF). Because EMF images are vector
based they can be scaled in the importing program without loss
of image resolution. EMF images can usually be ungrouped in
a CAD or drawing package (even PowerPoint) so different parts
can be resized, coloured or modified independent of the other
parts of the map.
When exporting maps in EMF format any labels and point symbols
should be created using a common font or they will not appear
correctly, or at all, when opened on another computers. If there
is no common font that has the necessary symbols then you can
convert Marker Symbols to polygons when exporting in ArcGIS
9.x. In the export dialog box there are options available at
the bottom of the screen one of the options under 'Format' is
to convert the symbols to polygons.
c. JPEG images are a raster format that is often used for presenting
information on the WWW, used on a variety of platforms/programs,
or can be modified in a graphics package such as PhotoShop.
JPEG images are preferred for colour images that will be used
on the WWW or some page layout programs.