ADDING SPATIAL INFORMATION: ADDING NON-SPATIAL DATA
|
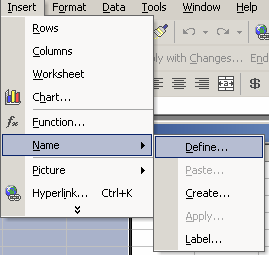
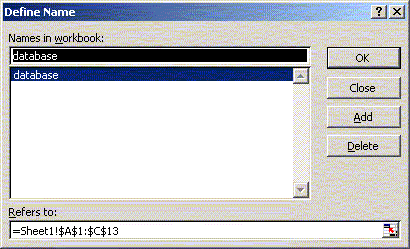
Adding Non-Spatial Data Along with creating tables based on your map’s themes, you can add already-existing Dbase IV (dbf), Access (mdb), or comma/tab delimited text (txt) files to your project. Using the Add Data button in ArcMap, open the D:\gis_course\rha\rha_stat.dbf file. This table of statistics will be added to your Project. MS Access files are read through the Microsoft Jet Engine. There are a few limitations on using MS Access files. Select queries created in MS Access must be saved as a table. Other types of databases and remote tables can also be accessed through an OLE DB provider and ODBC. I often use Excel to edit ArcView attribute or dbf files, even those associated with shape files since the table editor in ArcView is not very friendly. This is especially true if you want to convert field type (character to number), or add and edit fields/records. If you want to use Excel for editing the Dbase (dbf) files make sure you have defined the database range in the worksheet before saving. The database region is defined using the Insert>Name>Define menu. The cells should be appropriately formatted in excel as well – avoid using ‘General’ formatting.
Quote comma (csv) and Tab separated files can be used. ArcGIS will attempt to read the format of the text files and generate a schema.ini file. The first line in these files must contain the names of the fields. The type of the field, unless all values are in quotes, is determined by the content of the field. This can sometimes cause problems when you want a character string field that contains only numbers. If you cannot join two tables based on a field that appears to contain the same information in two tables check the type (character/numeric) of each field. Character fields are left justified, numeric fields are right justified. When bringing data from SAS the simplest method would be to save the file in DBF format using PROC EXPORT or PROC DBF, or as comma separated files using the _lotus macro. Most programmers at MCHP are familiar with the _lotus macro for saving comma or tab delimited files. The advantage to using the _lotus macro is titles and program information can be added. Extra titles and/or comments would have to be removed since ArcGIS would not understand what to do with those records. You can merge your tables using the join feature of ArcMap. The name of the common field does not need to be the same but the content must be the same. Typically you will want to add imported tables to a layer attribute table. Once tables have been joined the new fields will be available for mapping.
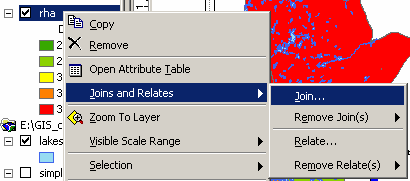
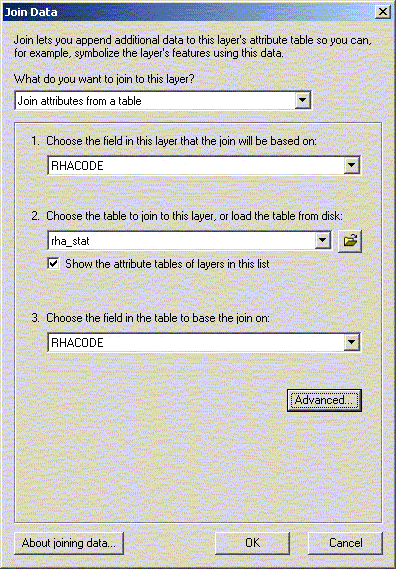
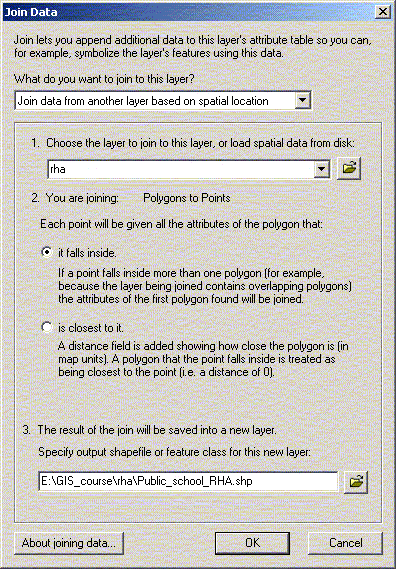
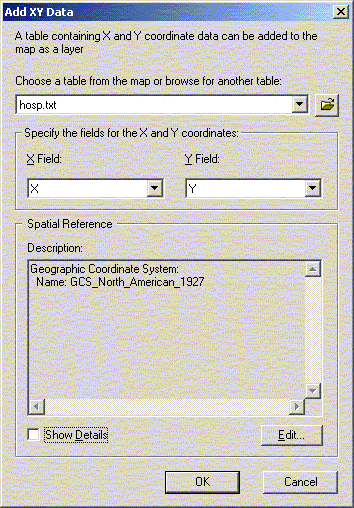
Spatial joins can be used to add RHA information to other themes (public schools for example). In fact, almost any two attributes tables can be joined with a spatial join. The exception is joining a point or line theme into a polygon theme. The spatial join can be used to measure distance between points – if you join two attribute tables of points or lines, the spatial join table will give you a column with the distance in map units to the closest point from the original table. If the underlying table contains a join you will need to remove it if you want to join the table to another. The underlying table in any given join cannot already be joined to anything. You can remove all or specific joins to a table by selecting remove from the join menu. There is a relate option within ArcMap for relating two tables. Unlike joining tables, relating tables simply defines a relationship between two tables. The fields of the source table are not appended into the fields of the destination table. After a relate is created, selecting a record in the destination table will automatically select the record(s) in the related or source table. Relates allow a one-to-many relationship to be established between two tables. Just as layers can be used to generate tables in ArcGIS, tables can be used to generate layers, as long as the table has X and Y (longitude/latitude) coordinates. In this case we will be creating a point layer. Line and Polygon layers can also be created from tables but the process is more complicated and will not be covered in this course. Under the tools menu choose ‘Add XY Data’ and open D:\gis_course\rha\hosp.txt file. For table, choose hosp.txt; for X and Y coordinates, choose X and Y. Click OK, and you should now have a new theme called hosp.txt. If you want to generate a theme from a table without X and Y coordinates, you can join it to a table with coordinates such as a postal code table. Open the shape file D:\gis_course\stat_can\sli_1.shp. Open Tables in the project window, and add D:\gis_course\rha\nursing_stations.txt. Now join the two tables (nursing_stations and attributes of sli_1) by postal code. When you join a larger table to a smaller table only those records from the active table are retained (see the help information for alternatives). Your nursing_stations.txt table now has X and Y coordinates, and you can create a nursing station layer through “Add XY Data” using Long and Lat as your X and Y coordinates. Note: In ArcView Version 8.2, to “Add XY Data”, you must first export the nursing_stations.txt table to a database file (dbf). Use the exported dbf to “Add XY Data” using Long and Lat as you X and Y coordinates.
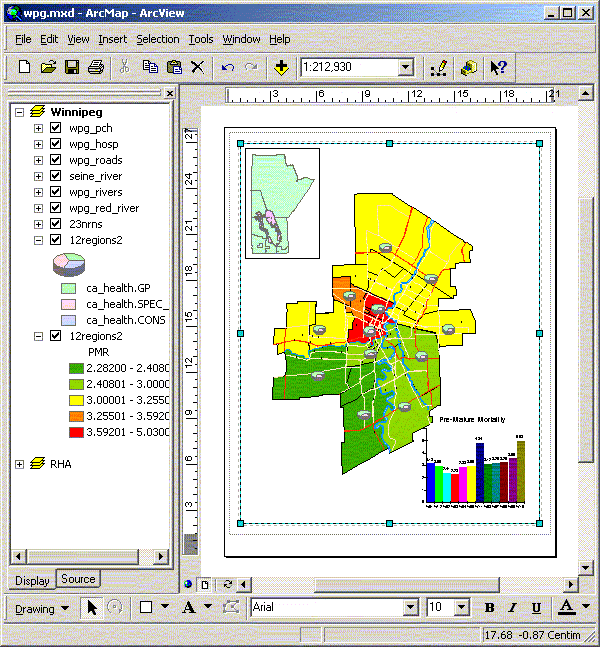
Open the WRHA map file and add the hospital locations (wpg_hosp) from the WRHA directory (D:\GIS_course\wrha) and the PCH shape (pch) from the RHA directory. Select only the Winnipeg PCHs and convert to a Winnipeg PCH shape (wpg_pch). Remember to set the selectable layers to only the PCH layer or you might select more than you expect. Open the ca_health data in excel just to see how the file is formatted the close the file without saving. Join the health measures table (ca_health) and social data (ca_social) to the community area geographies. Try mapping various values using different options for categories. Create a map of Winnipeg with a pie chart of GP, Consults, and Spec Visits for each CA Add a second Winnipeg CA theme and map the PMR. Add a second view that contains the Manitoba RHA areas using an appropriate projection. Modify the map in layout view with a chart of Winnipeg PMR, Manitoba RHA, and Winnipeg CAs with PMR and physician pie charts.
| ||||